Describe the Periodic Trends for Atomic Radius.
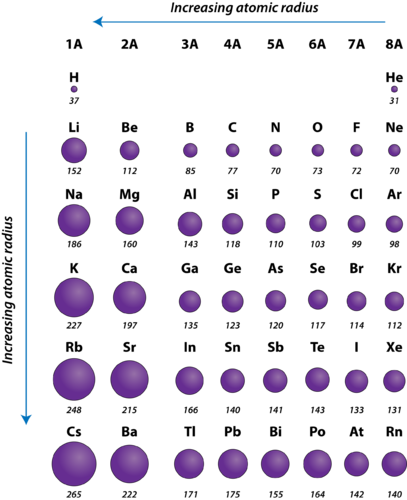
The atomic radius of an element tends to increase the further down you go in an element group. The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period.

Periodic Trends Made Easy Chemtalk
Describe the trends in atomic radii by checking the correct box.
. The chemistry and atomic structure of the elements is a contest between i nuclear charge conveniently represented by Zthe atomic number and ii shielding by other electrons. B Covalent radii of the elements are shown to scale. Identify which of the following atoms would have the largest radius.
There are some small exceptions such as the oxygen radius being slightly greater than the nitrogen radius. However this does not happen. The reason is that the probability for finding the electron never becomes zero.
An atom gets larger as the number of electronic shells increases. B Atomic radius decreases from left to right across the periodic table. The atomic radius is one such characteristic that trends across a period and down a.
And the atomic radius decreases. The precise measurement of the size of the atom is difficult because of the following reason. Because all the elements in a period are in the same energy level Electrons are the same distance away from the nucleus however because youre continually adding more protons the nucleus is better at attracting the electrons therefore decreasing the radius.
This is because the valence electron shell is getting larger and there is a larger principal quantum number so the valence shell lies physically farther away from the nucleus. 120 rows The distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an atom is known as the atomic radius. Major periodic trends include.
There are no sharp boundaries for the atomic orbital. Watch The recommended video to better understand atomic radius trends in periodic table. Periodic Trends Atomic Radius.
Describe the trend in ionization energy as the atomic number increases across a period. Atomic radius increases down the. You just studied 10 terms.
Atomic Radius Periodic Table Trends No matter what criteria you use to describe the atomic radius the size of an atom is dependent on how far out its electrons extend. Sr Zn Cl Be P Ive tried Be and P. Bachan Thakur October 5 2017 Leave a Comment.
This is because as we go down a group in the periodic table the atoms have increasingly more electron shells. What trend in atomic radius do you see as you go across a periodrow on the periodic table. Now it is a fact that the nuclear charge is SHIELDED very poorly by incomplete electronic shells.
Periodic trends arising from the arrangement of the. It is the sum of the individual covalent radii. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group.
Relative Atomic Radius In general as we move across the periodic table left to right the atomic radius decreases. Radius uparrow where PT stands for. Here is a look at the periodic table trends of electronegativity atomic radius electron.
Check all that apply. Periodic trends are specific patterns that are present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of a certain element including its size and its electronic properties. Graph II Ionization Energy 3.
Across a period the atomic size decreases as the number of shells remain the same while the nuclear charge increases. Periodic Table Trends Electronegativity Atomic Radius Ionization Energy. Atomic radius increases down a group.
The atomic radius gets bigger as the atomic number increases. Identify which of the following atoms would have the largest radius. Within a period protons are added to the nucleus as electrons are being added to the same principal energy level.
There are two main. Atomic radius increases down the periodic table. Atomic Radius Trend on the Periodic Table.
In the periodic table elements are categorized based on their electronic structure. Electronegativity ionization energy electron affinity atomic radius melting point and metallic character. Describe and apply the periodic trends for atomic radius.
Therefore the radius of the atom increases as one goes down a specific group in the periodic table of elements. This leads to the pulling of. The atomic radius gets smaller as you go across a period on the periodic table.
The size of an atom generally decreases as one moves from left to right for a certain period. What trend in atomic radius do you see as you go down a groupfamily on the periodic table. Use the periodic table to determine which elements are likely to have a larger atomic radius than silicon Si.
The number of protons also increases and there is relatively little extra shielding from electrons in the same shell. Graph I Atomic Radius 1. 119 rows Summary.
Many periodic trends are general. In general as we move down the periodic table the atomic radius increases. In general the atomic radius decreases.
Covalent radii can be used to estimate the bond distance between two different atoms. Describe the periodic trends for atomic radius. Up to 24 cash back 1.
Describe and apply the periodic trends for atomic radius. Based on the aforesaid relations the covalent radius of boron is. The distance between two oxygen atoms in molecular oxygen is 132 pm.
Explanation of atomic radius. In a group the atomic size increases due to the addition of shells as we move from one period to another. Larger the atomic radius larger the atom.
Because more protons are being added to nucleus the positive force is greater furthermore. Sr Zn Cl Be P Ive tried Be and P. Describe the trend in atomic radius as the atomic number increases down a group.
You might expect the atomic radius to increase because the number of electrons in each atom increases going across period 3. As you go down a column of the periodic table the atomic radii increase. Transition metals of the same period are roughly the same size.
In chemistry periodic trends are the tendencies of certain elemental characteristics to increase or decrease as one progresses along a row or column of the periodic table of elements. Atomic radii from the left to right across a period tend to. This makes the recurring element properties noticeable in this table.
Period 3 Na-Ar is the most suitable period for studying trends 1 ATOMIC RADIUS The atomic radius is basically used to describe the size of an atom. Describe the trend in atomic radius as the atomic number increases across a period. A Atomic radius increases from left to right across the periodic table.
Lets break down the trend into its period and group trends. Increase in atomic radii down a Group a column of the Periodic Table. Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table with Francium having the largest atomic radius.
Periodic Trends of Atomic Radii. This trend can be summarized as follows.
Atomic Radius Trend Periodic Table Chemtalk
Periodic Trends Atomic Radius Chemistry For Non Majors
What Are The Periodic Trends For Atomic Radii Ionization Energy And Electron Affinity Socratic
Comments
Post a Comment